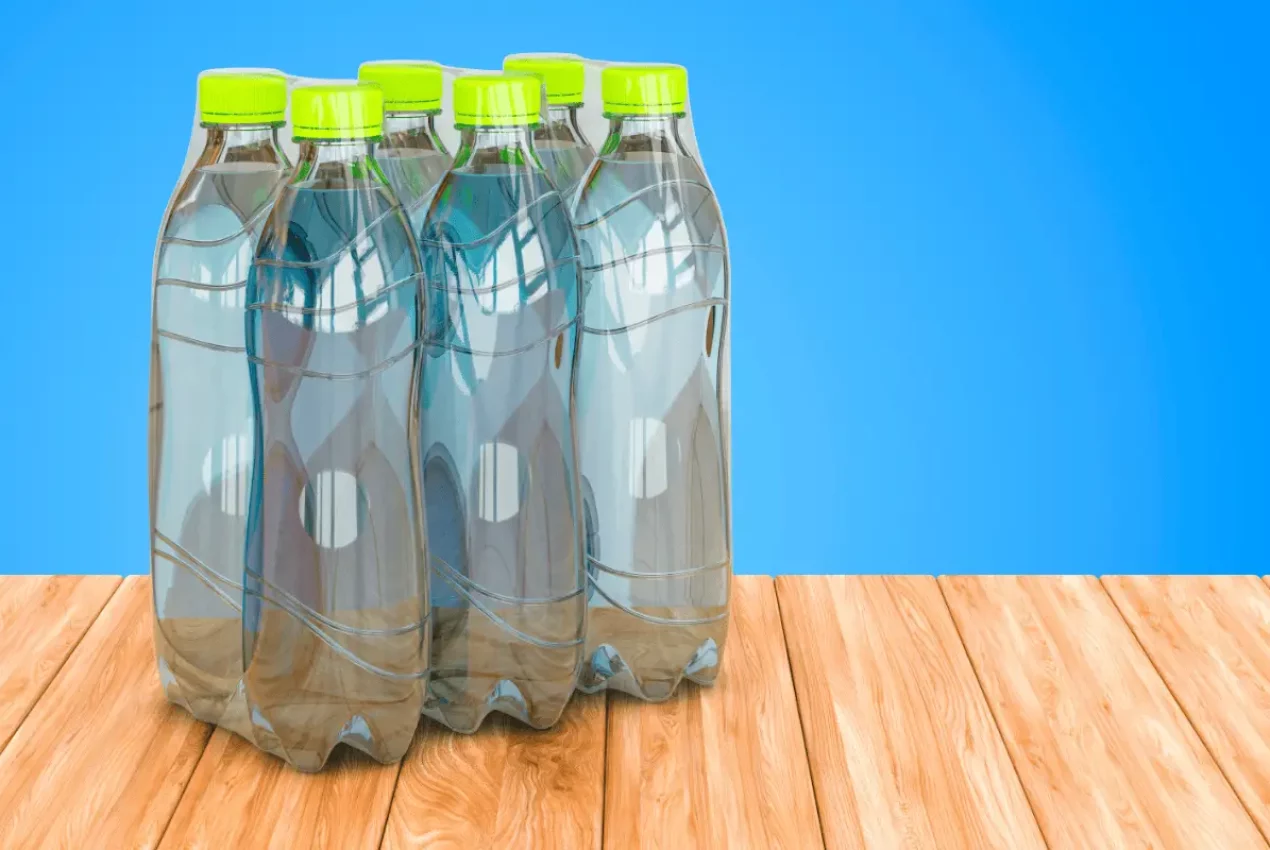
What Plastic Is Used in Shrink Wrapping?
 Three primary types of shrink wrapping exist for various applications in the shipping and retail industries, among others. These include polyolefin (POF), polyethylene (PE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each type of material comes with unique properties and benefits.
Three primary types of shrink wrapping exist for various applications in the shipping and retail industries, among others. These include polyolefin (POF), polyethylene (PE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each type of material comes with unique properties and benefits.
What Is Plastic Shrink Wrap Made Of?
The three types of shrink wrap materials offer different advantages that make them compatible with various applications. The following are the specific characteristics of each:
PVC Shrink Wrap
While PVC shrink wrap used to be the most popular shrink packaging material used for many applications, in recent years, its lack of sustainability and potential health hazards have made it less common than POF and PE shrink wrap materials. However, many applications still use it across multiple industries, with these materials composing the following:
- Clamshell packaging
- Blister packaging
- Bagging
- And other packaging materials
POF Shrink Wrap
POF shrink wrap is considerably safer than PVC shrink wrap and offers superior versatility and durability compared to other shrink wrap materials. Its food-safe nature has led the FDA to approve it for use in many applications. POF shrink wrap consists of polyolefin, which provides reliable protection for a wide variety of products, including those with an irregular shape. This material is also cost-effective and puncture-resistant, further contributing to its popularity.
PE Shrink Wrap
For applications requiring more flexibility than polyolefin shrink wrap but with the same level of durability, PE shrink wrap offers a dependable alternative. Polyethylene is a kind of polyolefin with added ethylene that allows for increased flexibility, making it ideal for shrink wrap and stretch wrap materials. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are available, with the increased durability and strength of LDPE offering more reliability for shrink wrap materials.
The Difference Between Shrink Wrap and Stretch Wrap
Although people often confuse plastic shrink wrap and stretch wrap because of their similar appearance, they each feature unique properties that result in differences in performance. In shrink wrap applications, packaging equipment places a thin film of PE over one or more products. The system then applies heat to the film, causing it to shrink over the items and forming a protective seal that’s resistant to tampering and tears. Stretch wrap applications, on the other hand, rely on a different type of formulation to allow for enhanced stretching.
Stretch wrap offers elastic memory and self-clinging capabilities to form a tight protective layer around products. It’s often used for unitizing or palletizing several products on pallets to keep them stable during transport. Another key difference between shrink and stretch wrap is the stretch limit before breakage occurs. For shrink wrap, this limit is a 50-75% stretch while stretch wrap can stretch to around 100-300% before breaking.
Why Polypropylene Is Less Used for Shrink Wrapping
Many applications forgo the use of polypropylene for shrink wrapping due to its increased hardness compared to other materials. Additionally, shrinking polypropylene leads to decreased stability and it has a higher melting temperature than other more reliable materials.
Shrink Wrap Products from Econo-Pak
If you need high-quality shrink wrap materials for your application, it’s important to determine which material is best suited for your project. Depending on what you need, Econo-Pak can help you select the right solution.
Let's start scaling.
Is your demand outpacing your ability to package your own product? Then consider outsourcing with Econo-Pak.
With over 40 years of experience working with both small brands and Fortune 500 companies, we are capable of handling your specific dry food product.
Get in touch with our team for a fixed-price quote for your project.